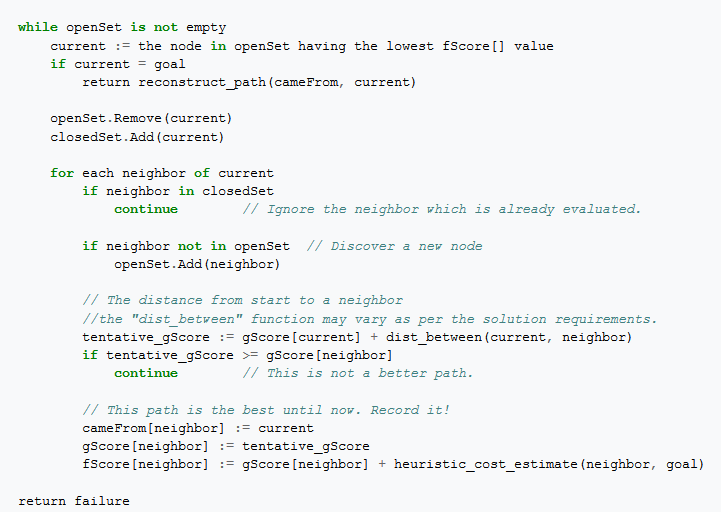
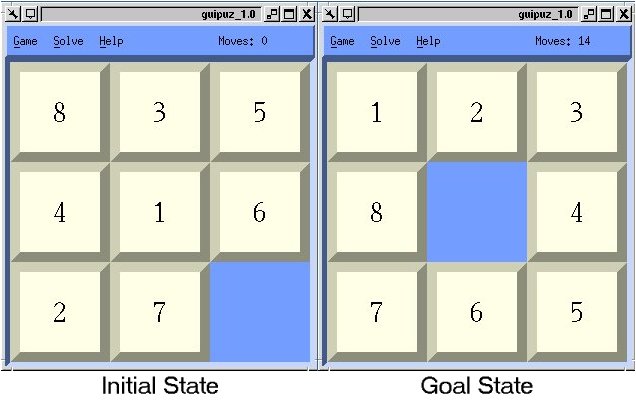
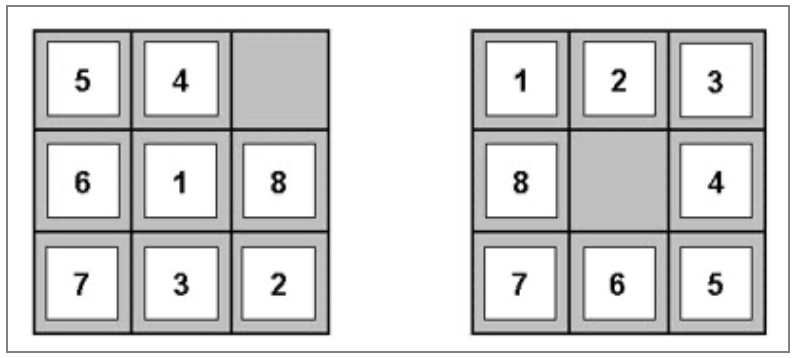
1 3 2 4 5 6 8 7 and goal state 1 2 3 8 4 7 6 5 i want to print out the running steps which solve this puzzle from initial to goal state this is the code i have so far.
Hueristic to solve a siding puzzle.
Admissible heuristic let h n be the cost of the optimal path from n to a goal node the heuristic function h n is admissible 16 if.
I am looking for code in java that implement a algorithm for the 8 puzzle game by given initial state.
If you start with the top row and the left column you can solve slide puzzles of any size by breaking them into smaller and smaller grids.
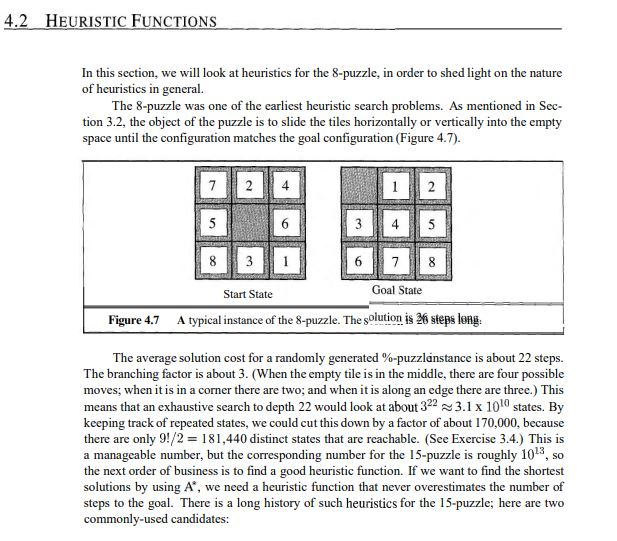
The puzzle is divided into n 1 rows and n 1 columns eg.
Sliding puzzle nxn solver.
For more info on ai and its algorithms get the book artificial intelligence.
Keep solving the top row and leftmost column as many times as necessary until you have a 3x2 grid with five tiles left to arrange.
15 puzzle will have 4 rows and 4 columns an 8 puzzle will have 3 rows and 3 columns and so on.
N puzzle or sliding puzzle is a popular puzzle that consists of n tiles where n can be 8 15 24 and so on.
Good guide to the heuristic s overall usefullness.
Sliding puzzles can be incredibly difficult to solve as anyone who s tried can tell you.
I am a student so i may be completely off base here.
0 h n h n an admissible heuristic function is always optimistic.
Sliding puzzle this application finds the optimal solution to solve a 8 or 15 puzzle.
To compare the admissible heuristics mentioned earlier h1 to h4 one can generate a large number of initial states for the 8 puzzle and solve each one using all 4 heuristics.
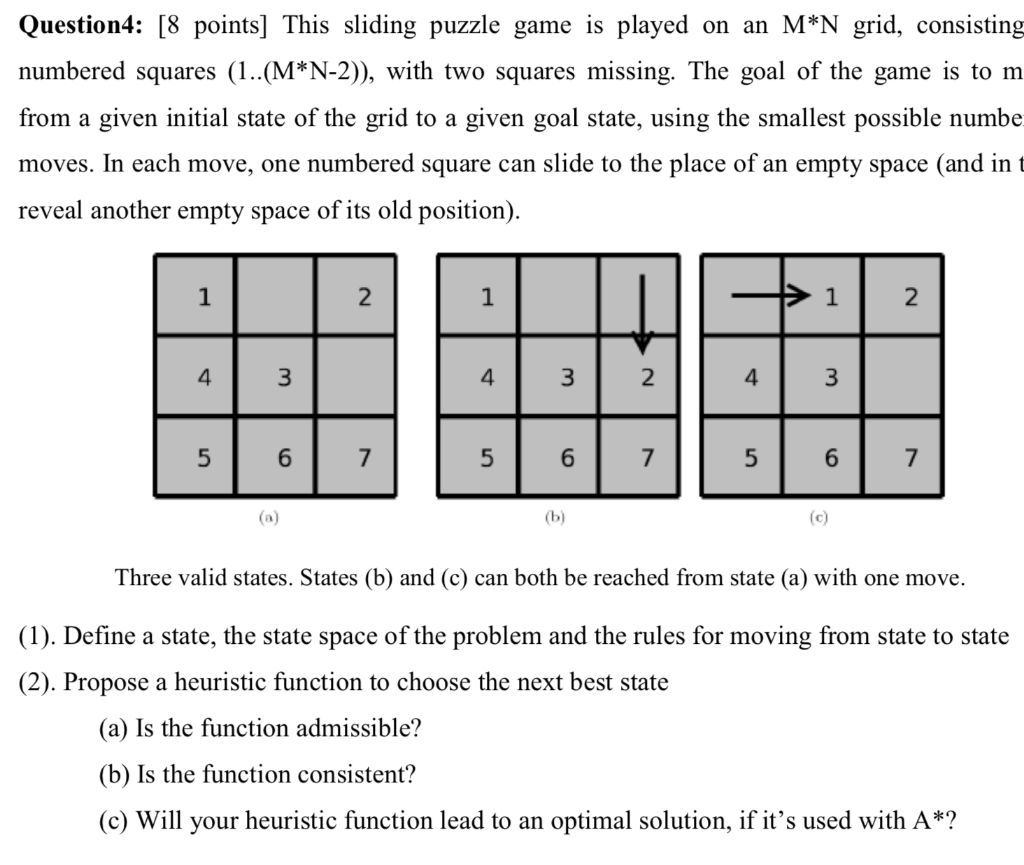
The puzzle consists of a n x m board shown in figure 1 where each cell could be represented as a number a letter an image or basically anything you can think of.
Mathematicians categorize sliders as pspace complete which is a measure of their mathematical complexity.
The number of nodes expanded and depth of solution.
The current state as a list goal state as a list current level parent state and the used heuristic function and once it is initialized the heuristic score.
To solve it by computer or ai we need a bit of a basic understanding of how it works to get the goal node.
A employs a heuristic function to find the solution to a problem.
Essentially it means that even computers find it hard to come up with a solution source.
Implementation for a star and bfs algorithms to solve a nxn grid sliding puzzle problem.
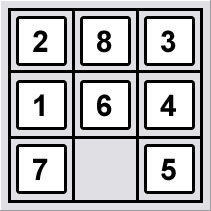
A 3 x 3 sliding tiles puzzles board.
It takes the following arguments.
Click on image for larger view figure 1.
G is a goal node îh g 0 h n number of misplaced tiles 6 8 puzzle heuristics 4 1 7 5 2 3 6 8 state n 4 6 7 1 5 2 8 3 goal state.
By optimal solution we mean a solution requiring the minimum numbers of moves.
Solving 8 puzzle manually varies from person to person.
A well designed heuristic would have a value of b close to 1.
Gamestate class describes any game state in the search space.